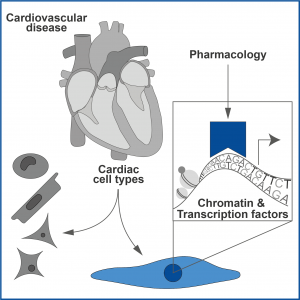
The main research focus of our group is to develop new approaches for cell type-specific pharmacological targeting of cardiovascular disease. The heart is a heterocellular organ that composes of multiple cell types, including cardiac myocytes, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and immune cells. We aim to understand cell type-specific functions in cardiovascular physiology and disease, from chromatin remodeling, transcription factor activity, and gene expression to in vivo experiments and translational or clinical studies.
Pharmacology of the mineralocorticoid receptor
Mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonists are a cornerstone of heart failure therapy. However, adverse effects related to concurrent MR inhibition in the kidney preclude the use of current MR antagonists in many patients. Therefore, novel approaches that specifically target the MR signaling pathway in the heart vs the kidney are needed. The mineralocorticoid receptor belongs to the family of ligand-activated transcription factors und elicits most of its activities through regulation of gene expression. We could show that the mineralocorticoid receptor mediates distinct effects in different cell types such as cardiac myocytes or endothelial cells that contribute to the pathophysiology of heart disease.
The goal of our research is to understand the molecular function of MR in different cell types and to identify epigenetic mechanisms or co-regulatory factors that might serve as organ-selective targets within the MR signaling pathway.
Clarisse […] Lother. Br J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34698367
Mamazhakypov, Hein, Lother. Pharmacol Ther. 2021 PMID: 34480966
Kowalski & Deng […] Lother. Hypertension. 2021;78(2):456-465 PMID 33966455
Lother et al. J Endocrinol. 2019;240(1):15-26. PMID:30400069
Lother et al. Cardiovasc Res. 2018;114 (2):282-290. PMID:28430882
Lother & Hein L. Hypertension 2016;68 (1):6-10. PMID:27217405
Epigenetic regulation of endothelial cell biology
Endothelial cells constitute a large proportion of non-myocyte cells in the heart and are today considered to be key regulators in the cardiovascular system. They contribute to all major cardiovascular diseases, from atherosclerosis to coronary artery disease and heart failure. In previous studies, we could show that the cardiac endothelial cell transcriptome is highly cell type- but as well organ-specific, reflecting the distinct biological function of endothelial cells in different organs.
We aim to elucidate how epigenetic mechanisms determine cell type-specific gene expression and function of cardiac endothelial cells and to evaluate their potential as new biomarkers or therapeutic targets.
Deng L […] Lother A. Sci Adv. 2024;10(10):eadj5101. PMID: 38446896
Lother et al. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 38 (3):566-574. PMID:29301788
Lother et al. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 151:74-87 PMID 33197445
Translational and clinical studies
Acute or chronic heart failure are frequent and associated with substantial mortality. We link experimental data to translational or early clinical studies to discover biomarkers, develop innovative therapeutic approaches, or broaden indications of established therapies. We are in particular interested in intensive care and acute cardiovasculare medicine.
Biever […] Lother. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2021;9(2):e00743. PMID 33710753
Rieder […] Lother. Am J Hypertens. 2021;34(3):278-281. PMID: 33043967
Supady […] Lother et al. Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9(7):755-762. PMID: 34000236
Rieder […] Lother. J Infect Dis. 2021;223(5):775-784. PMID: 33249471
Lother & Hein. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016;166 :136-49. PMID:27456554
Key techniques
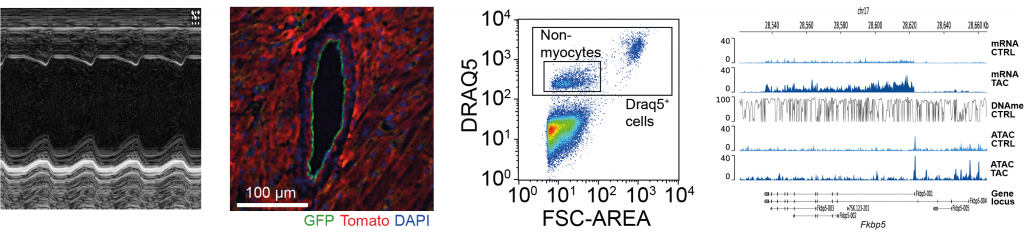
- in vivo studies (echocardiography, RV/LV pressure catheterization, ECG/blood pressure telemetry, pressure overload, agonist/antagonist treatment, in vivo hypoxia/hyperoxia chamber)
- Cell/nuclei isolation (FACS, FANS, MACS)
- Gene expression & chromatin analysis (RNAseq, ATACseq, ChIPseq, Cut&Run, RIME, Bioinformatics)