Gene expression networks in endothelial cells from failing human hearts
Chronic heart failure is associated with adverse remodeling of the heart that is typically characterized by cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. This requires the formation of new capillaries to maintain oxygen supply. Insufficient...
Cardiac injury and gene expression induced by catecholamine treatment is largely reversible
Catecholamines are commonly used as therapeutic drugs in intensive care medicine to maintain sufficient organ perfusion during shock. However, excessive or sustained adrenergic activation drives detrimental cardiac remodeling and may...
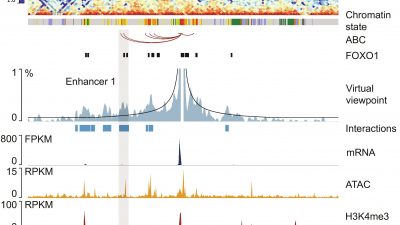
Epigenome and 3D chromatin structure of cardiac endothelial cells
Endothelial cells play crucial roles in physiology and are increasingly recognized as therapeutic targets in cardio-vascular disease. Here, we analyzed the regulatory landscape of cardiac endothelial cells by assessing chromatin...
2024 Joint Meeting of ESAC & ADMIRE Network
Registration and abstract submission for the 2024 Joint Meeting of ESAC and the ADMIRE network is now open: meeting.admire-network.org...
Molecular pharmacology of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists
Mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonists have shown remarkable benefits in the treatment of cardiovascular disease. However, their underutilization in clinical practice may be attributed to concerns regarding the risk of hyperkalemia...
Cell types of the heart: identities, interactions, and implications for cardiology
The heterocellular nature of the heart has been receiving increasing attention in recent years. In addition to cardiomyocytes as the prototypical cell type of the heart, non-myocytes such as endothelial...