Downregulation of TCF19 and ATAD2 causes endothelial cell cycle arrest at the transition from cardiac hypertrophy to heart failure
Increased load leads to cardiac hypertrophy and endothelial cells play a vital role in maintaining oxygen supply to the heart through angiogenesis. However, insufficient angiogenesis contributes to the progression of...
Cell Type–Resolved Transcriptome of Aldosterone-Induced Atrial Myopathy and Arrhythmia
There is emerging evidence that mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists reduce the burden of atrial fibrillation in patients with or without heart failure. In this study, we show that aldosterone infusion drives...
Gene expression networks in endothelial cells from failing human hearts
Chronic heart failure is associated with adverse remodeling of the heart that is typically characterized by cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. This requires the formation of new capillaries to maintain oxygen supply. Insufficient...
Cardiac injury and gene expression induced by catecholamine treatment is largely reversible
Catecholamines are commonly used as therapeutic drugs in intensive care medicine to maintain sufficient organ perfusion during shock. However, excessive or sustained adrenergic activation drives detrimental cardiac remodeling and may...
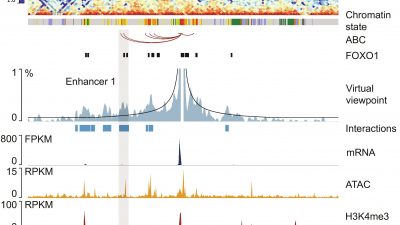
Epigenome and 3D chromatin structure of cardiac endothelial cells
Endothelial cells play crucial roles in physiology and are increasingly recognized as therapeutic targets in cardio-vascular disease. Here, we analyzed the regulatory landscape of cardiac endothelial cells by assessing chromatin...